Product and Pipeline
More effective combination treatments for cancer
Cancers are complex dynamic and adaptive diseases with the tumor micro-environment comprising many different cell types, matrix proteins and secreted molecules.
The interplay between these elements impacts the responsiveness to therapy and whether there is continued tumor survival and progression, even in the face of continued treatments. We believe that remodelling of the tumor microenvironment and taking a multi-pathway and multi-target approach offers an opportunity to significantly improving response rates and durability of response.
Oncology Pipeline
Description
| Product – Indications | Preclinical | Phase 1 | Phase 2 | Phase 3 | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP-002 Platform | |||||
| SP-002: Phase 3 Basal Cell Carcinoma (H-Zone) | Planning – to commence in 2025/26 | ||||
| SP-002: Phase 2B Locally Advanced BCC | On-going | ||||
| Vector-Drug Conjugate Platform | |||||
| SP-537 Pancreatic Cancer | |||||
| SP-563 Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer | |||||
SP-002
SP-002 is an adenoviral vector (serotype 5, Ad5) encoding the therapeutic cytokine Interferon-γ. The vector has been engineered to be replication-deficient so it can transduce cells and produce Interferon-γ, but not new viral particles (a safety feature not present in oncolytic viruses).
Recombinant Interferon-γ protein has shown superior potency in tumors when compared with Interferon-⍺, however, its successful clinical application in cancer has been hampered by its narrow therapeutic window. The main advance of SP-002 is a wider therapeutic window as transduced tumors release a therapeutically-effective dose of IFN-γ locally, without causing significant systemic toxicities.
Nodular Basal Cell Carcinomas in the H-zone
SP-002 is being developed as a novel intralesional therapy for patients with nodular BCCs located in the H zone. These are lesions that have a high-risk of recurrence and/or require major reconstruction or result in significant morbidity/dysfunction with surgery. SP-002 may also be suitable for patients that are considered not good candidates for surgery, due to medical reasons or patient preferences.
It is estimated that 3-4 million cases1 of Basal Cell Carcinomas arise annually in the US, of these an estimated 60-80% are Nodular Basal Cell Carcinomas2, of which ~20-40% are located on the H-zone3 or other high-risk anatomical sites or occur in patients that are not good candidates for surgery, due to medical reasons or patient preferences. It is estimated that an annual population of up to 857,000 patients annually in the United States may be addressable with SP-002 for this patient subset.
SP-002 with a Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitor (HHPI)
Locally Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma
The combination regimen is being developed as an effective treatment for Locally Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma. Basal cell carcinoma is a common skin cancer, with up to 3-4 million cases1 arising annually in the US. About 2% of these patients progress to advanced disease (about ~60,000 per yr. in the US).2 LA BCC comprise unresectable lesions, recurrent (multiple recurrences) lesions and lesions on anatomically difficult surgical sites that would result in significant functional damage upon resection.
Clinical Rationale
The HHPI (Hedgehog pathway inhibitors, e.g., vismodegib and sonidegib) are FDA-approved agents for use in LA BCC when surgery and radiotherapy are not suitable. Of the estimated that of 60,000 LA BCC patients, only a small subset use HHPIs. The primary reason for HHPI’s low adoption rate is the low Complete Response (CR) rate observed. HHPIs are effective at shrinking a majority of LA BCCs, but residual BCC persist within treatment.
SP-002 with HHPI have a synergistic mechanisms of action and is anticipated to improve both CR rate and durability of response.
Rationale for add-on of SP-002 to HHPIs
HHPI Monotherapy – major ‘debulking’ of large BCCs
BCCs are heterogeneous with respects to HHPI responsiveness 1-3
HHPI highly effective in majority of BCCs 1-3
HHPI resistant residual BCC can lead to relapse ~CR~20-30% 5
Quiescent residual BCCs express LGR5 cancer stem cell marker 1-3
HHPI & SP-002 Combination Therapy – ‘debulking’ and removal of HHPI resistant residual populations
HHPI
HHPI plus SP-002
Interferon – γ ablating residual BCCs (Interferon – γ reported to induce cell death in LGR5 stem cells) 4
Complete Responses Targeting CR >40-50%
1 Eberl et al, Cell 2018 33, 229
2 Biels et al, Nature 2018 562:429
3 Sánchez-Danés, Nature 2018 562:434
4 Takashima, et al Sci Immunol 2019 4:42
5 vismodegib product information sheet
SP-500: Vector Drug Conjugate Platform
Vector Drug Conjugates – Improving Clinical Benefit & Tolerability
Novel vector design
The SP-500 platform is based on Adeno-vectors conjugated with small molecule payloads that demonstrate significant synergies with Interferon-γ
Advantages of Vector Drug Conjugates
- Improved therapeutic window compared to systemic or intralesional administration of small molecule chemotherapeutic
- Co-delivery of both genetic and small-molecule payloads offers greater targeting flexibility
- Vector Drug Conjugates have a high-payload capacity and engineered linkers adds target selectivity
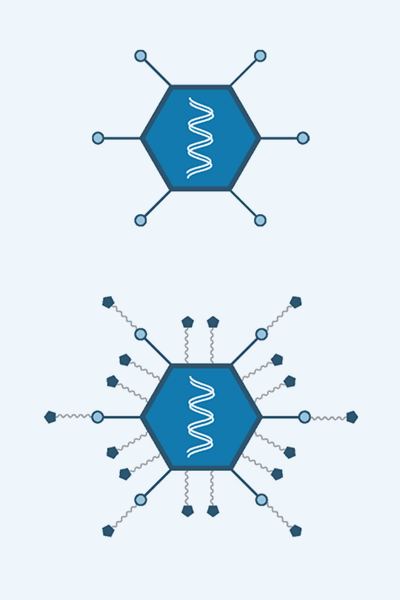
SP-500 Platform – Vector Drug Conjugates Engineered to Induce Multiple Programmed Cell Death Pathways
- The hAd5-IFN-γ vector core-platform has already demonstrated safety and an efficacy signal in human clinical studies
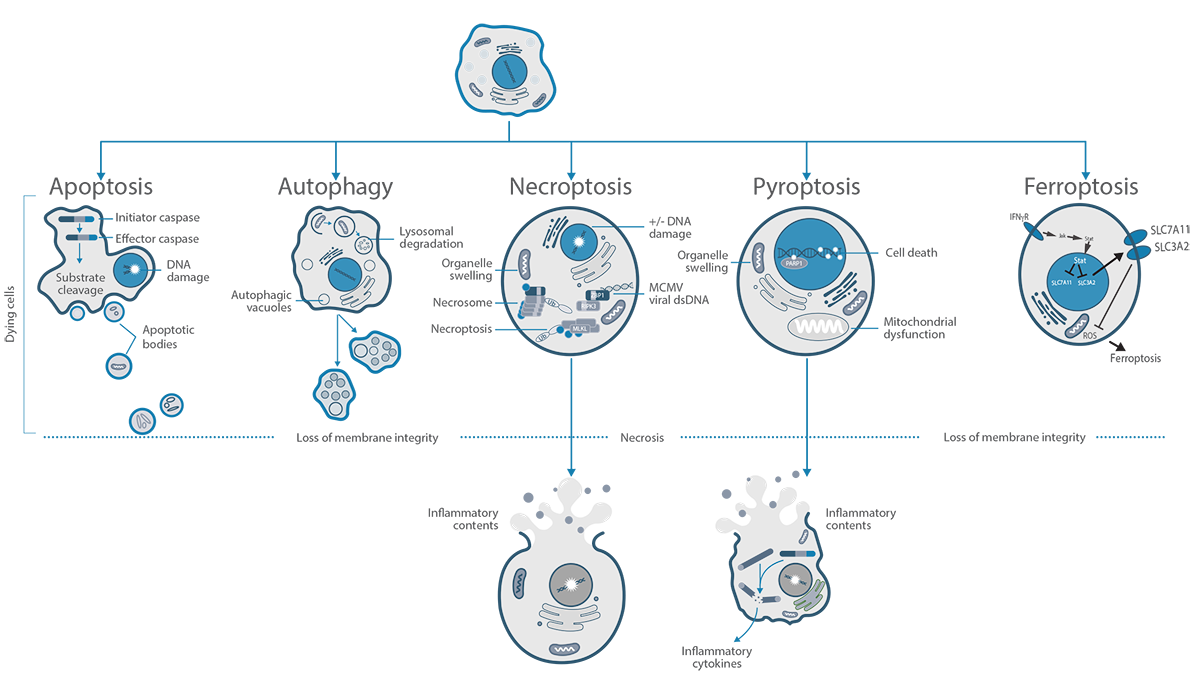
- The SP-500 platform is designed to induce programmed cell death via multiple pathways.
SP-563
Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
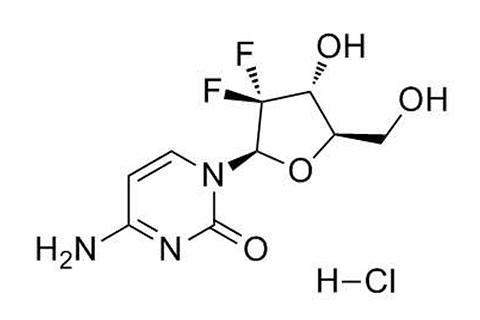
Rationale: Interferon Synergizing with Gemcitabine
- hAd5-IFN-γ vector platform has a good safety and efficacy signal across multiple clinical trials and cancers
- hAd5-IFN-γ vector platform has been shown to be efficacious in vivo in bladder cancer xenograft models (SW-780 in nude mice)
- Gemcitabine is a pyrimidine nucleoside antimetabolite that inhibits DNA synthesis and causes apoptosis
- Gemcitabine is an approved standard of care for bladder cancer
- Gemcitabine has IC50 in the low nM range in multiple cancer types
- Synergy between IFNγ and Gemcitabine demonstrated in multiple studies
- The combination can induce multiple pathways of programmed cell death
Stage: Preclinical
SP-537
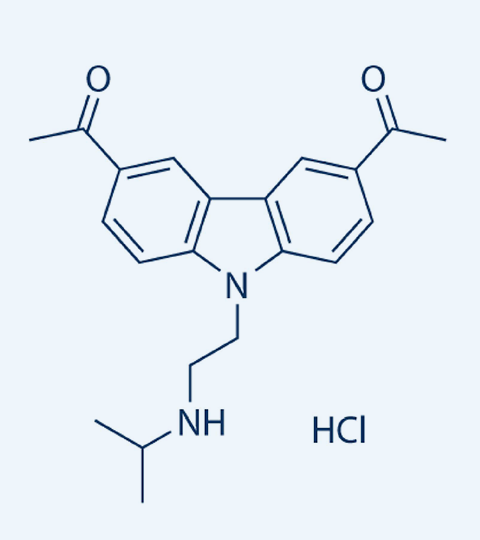
CBL-0137 MOA: Disrupts DNA-histone and Interferes with Enhancer-Promoter Interactions
- Destabilizes DNA/histone interactions, nucleosome disassembly and chromatin decondensation 1
- Inactivates FACT and reduces transcription of NF-kB, HSF1, HIF1α, MYC & activation of p53 2
- Induces Z-DNA formation leading to ZBP1 activation and necroptosis 3
- IFN-γ (hAd5-IFN-γ) is a potent inducer of ZBP1 in myeloid (MDSCs) and CAF populations 4
- Highly-efficient depletion of both intra-tumoral CAFs & MDSC 4,5
- CBL0137 evaluated in prostate, colon, renal cell carcinoma, medulloblastoma, small-cell lung cancer, and melanoma 6
Stage: Preclinical
References
- Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(4):1925–1945. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1366.
- Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(95):95ra74. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002530.
- Nature 2022 Jun;606(7914):594-602.doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04753-7.
- Nature. 2007;448:501–505. doi: 10.1038/nature06013. published online; SP data available under NDA.
- Cancers (Basel) 2024 Nov 3;16(21):3711. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213711.
- https://clinicaltrials.gov



